带宽与速率的区别(Bandwidth and Data Rates)
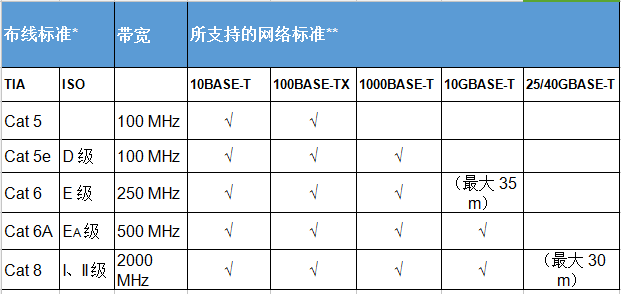
When it comes to copper cabling, you’ve probably heard of Category 6 as having a bandwidth of 250 MHz and Category 6A as having a bandwidth of 500 MHz. (The bandwidth is often printed on the cable jacket.) This creates plenty of confusion since we think of bandwidth on the network as expressed in Mb/s or Gb/s. We are not wrong in that mindset – your Category 6A cable may have an operating bandwidth of 500 MHz, while your network may have a bandwidth of 10 Gb/s.
说到铜缆,你可能听说过6类的带宽是250MHz,6类的带宽是500MHz(带宽通常打印在电缆护套上。)这造成了大量的混乱,因为我们认为网络上的带宽是以Mb/s或Gb/s表示的。我们的想法并没有错——您的6A类电缆的工作带宽可能为500 MHz,而您的网络的带宽可能为10 Gb/s。
So why is category cable bandwidth defined as MHz? Good question. Megahertz is the frequency or rate at which a wave will cycle each second, with 1 hertz equal to 1 cycle per second and 1 MHz equal to 1 million cycles per second. The relationship of speed to frequency is a bit complex, but in simple terms, higher frequencies are needed to carry more bits of data. Each data bit is encoded on a carrier frequency, and the amount of data that can be transmitted per second depends on the signal encoding scheme of the active equipment.
那么,有同学会问为什么类别电缆带宽定义为Mhz?这是个好问题。兆赫是波每秒循环的频率或速率,1赫兹等于每秒1个循环,1兆赫等于每秒100万个循环。速度与频率的关系有点复杂,但简单来说,需要更高的频率来承载更多的数据位每个数据位在载波频率上被编码,并且每秒可以发送的数据量取决于有源设备的信号编码方案。
Back in the days of Cat 5, the bandwidth and the data rates were the same – 100 MHz cabling could deliver 100 Mb/s. But designers of network interfaces have been able to develop encoding schemes such as pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) and DSQ128 to go beyond the simple 1:1 relationship of bandwidth to data rate. By the time Cat 6 came out, they were able to drive 10 Gbps over a cable with a bandwidth of 250 MHz. This approach is how NBASE-T is able to get 2.5 and even 5 Gbps out of Cat 5e cable and how your cable provider gets you faster internet speeds without recabling the connection to your house.
早在第5类的时代,带宽和数据速率是一样的——100兆赫的电缆可以传输100兆字节/秒。但是网络接口的设计者已经能够开发编码方案,如脉冲幅度调制(PAM)和DSQ128,以超越带宽与数据速率的简单1:1关系,到Cat 6问世时,他们已经能够通过一根带宽为250mhz的电缆驱动10gbps这种方法是NBASE-T如何能够从5e类电缆中获得2.5甚至5 Gbps,以及您的电缆供应商如何在不重新布线的情况下,为您提供更快的网速。
同类文章排行
- 带宽与速率的区别(Bandwidth and Data Rates)
- EXFO的OTDR测试仪区别MAX-715B/MAX-720C/MAX-730C/FTB
- 如何检验福禄克跳线适配器性能?
- 福禄克FLUKE DTX-PCTAC5EKS/DTX-PCTAC6KS/DTX-PCTAC6AKS/DSX-PCTAC6AKS何时需要更换?
- 福禄克FLUKE DSX2-8000/DSX2-5000跳线测试与通道测试的区别?
- 解读您网线Fluke测试报告
- 边缘测试
- 福禄克FLuke Ti25 T i32 TIS75 TI401PRO Ti450 Ti480PRO红外热像仪对比
- 关于GBT50312-2016综合布线 GBT21671-2018局域网(LAN)系统验收GBT32420-2015无线局域网测试规范设备选型的NetAlly和FLUKE方案
- 用于将成像仪连接到 PC 的福禄克热成像驱动程序
最新资讯文章
您的浏览历史








